Dry foods, such as pistachios, spices, cereals, and milk powders, may appear low risk due to their lack of moisture. But in reality, they can harbor dangerous pathogens like Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and E. coli O157:H7 that can survive for long periods in dry environments (1,2). These organisms don’t need water to persist, and some, like Salmonella, can become more heat-resistant when suspended in low-moisture, high-fat food matrices (3)......
We are pleased to announce that our latest peer-reviewed research article, “Construction and Functional Characterization of a Heterologous Quorum Sensing Circuit in Clostridium sporogenes,” has been officially published in ACS Synthetic Biology....
Food manufacturers know that a product’s shelf life is critical for quality, safety, and brand reputation. Yet microorganisms – bacteria, yeasts, and molds – can quietly sabotage shelf life, causing spoilage, food safety hazards, and even costly recalls. ...
On August 15, 2025, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) released an update on the ongoing outbreak of Salmonella ...
On August 15, 2025, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) released an update on the ongoing outbreak of Salmonella ...
Engineers and biochemists at McMaster University have developed a biogel test that allows untrained users to detect bacterial contamination in ...
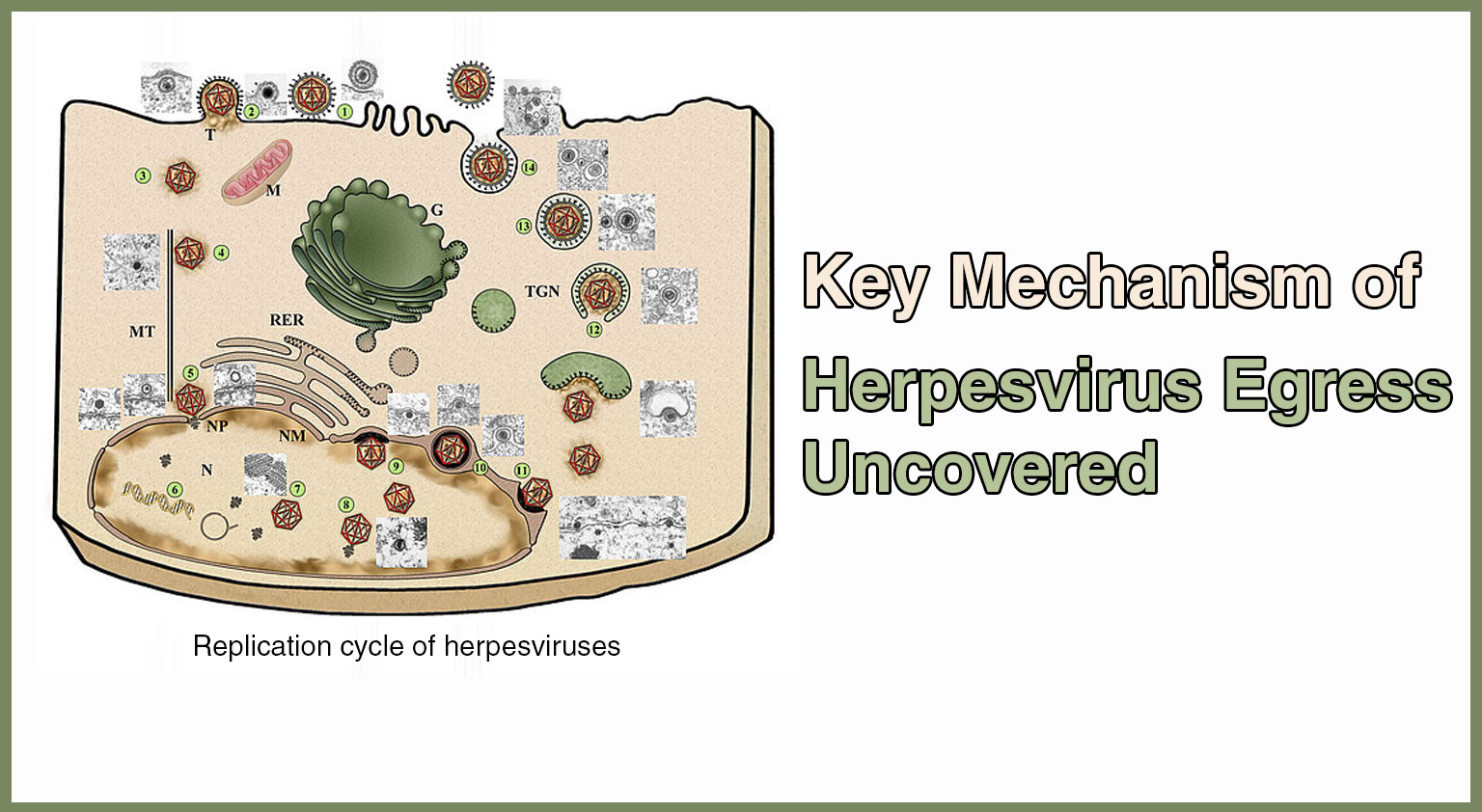
A recent study published in Nature Microbiology on June 25. has shed light on a critical aspect of herpesvirus infections. Herpesviruses are a widespread family of viruses ...
Researchers at Nofima developed a faster method to detect Listeria monocytogenes in food products, which is a significant challenge for the ...
The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) is investigating a multi-province outbreak of Salmonella infections linked to certain Genoa salami products ...
CREM Co Labs is excited to announce its participation in the APIC 2025 Annual Conference & Expo in Phoenix ...
We are pleased to let you know that CREM Co Labs will be exhibiting at IPAC Canada 2025 in Winnipeg, May 30–June 3. We’d love to welcome you at Booth #44 to share Infection Prevention & Control Research, Efficacy and Stability Testing Services, Pathogen ...
In 2024, Health Canada revised the monograph for Antiseptic Skin Cleansers intended for Personal ...
In this series of articles, we compare the previous 2020 efficacy guidance with the new efficacy requirements for biocides—highlighting what has changed and what these changes mean ...
Researchers from the Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland (HIPS) and the German Center for Infection research (DZIF) ...
A new study published in Microbiology Spectrum highlights a new, streamlined workflow that can detect low levels of Listeria monocytogenes in food samples within 8 hours. Currently ...
New peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Virological Methods expands CREM Co Labs’ large-chamber aerobiology protocol from bacteria, and virus surrogates to mammalian viruses